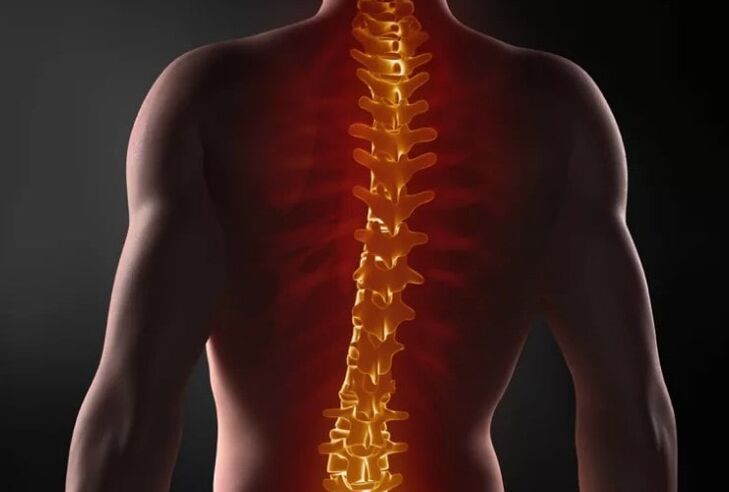
Osteochondrosis of the spine is a fairly common disease in the modern world. In the past, osteochondrosis was mainly seen in patients after the age of 35-40. Diagnosed at an early age, it has now become significantly younger and is already being diagnosed in young people aged 18-20. The rejuvenation of the disease is associated with the emergence of various devices with which young people spend a lot of time. A sedentary and sedentary lifestyle is considered the main reason.
What is Osteochondrosis?
Osteochondrosis of the spine is a chronic disease in which degenerative changes occur in the vertebrae and intervertebral discs and other tissues of the spine. Spinal osteochondrosis is divided into three types depending on the area of damage to the spine:
- osteochondrosis of the cervical spine;
- thoracic department;
- Lumbar spine.
Due to the injury, compression of the intervertebral discs by the vertebrae occurs, leading to dysfunction of the intervertebral disc itself. The result of such processes over time is that the nerves in the back become pinched and pain, swelling, cramps and other symptoms occur.
Causes of osteochondrosis
Let's talk about the factors contributing to the occurrence of this disease:
- lack of exercise;
- Physical overexertion;
- Incorrect posture when sitting. This reason is one of the most popular;
- hypothermia of the body;
- Carrying a heavy bag or backpack on one shoulder;
- Neuroemotional exhaustion (depression, neuroses)
- sleeping on a soft or uneven surface;
- Unbalanced diet, lack of nutrients (vitamins, minerals, etc. )
- Problems with digestion and metabolism, due to which nutrients necessary for the normal functioning of the body are absorbed;
- obesity;
- back injuries;
- flat feet or other lower extremity problems;
- genetic predisposition;
- Incorrect posture;
- Smoke;
- Wearing uncomfortable shoes;
- One of the causes of this disease can be multiple pregnancies.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis
- Pain in the diseased part of the spine in the acute stage, it can be very acute or painful;
- muscle cramps;
- Numbness of the upper or lower extremities, loss of sensitivity, depending on which part the problem is. Most commonly, fingers or toes become numb;
- Headaches and dizziness most often occur due to problems in the cervical or thoracic spine;
- Stiffness, pain when moving the body in some positions;
- Increased fatigue;
- Increased temperature in the affected area;
- So-called lumbago (stinging pain), especially when lifting heavy objects or making sudden movements;
- Poor posture;
- Pain in chest and ribs – intercostal neuralgia;
- Increased blood pressure and body temperature;
- Pain in the area of the heart or ribs is due to pinched muscles;
- Goosebumps and tingling in the spine;
- The appearance of "floaters, " black or colored spots in front of the eyes.
Diagnosis of osteochondrosis
As a rule, a neurologist makes the diagnosis based on various studies:
- First, the patient is interviewed and examined;
- Neurological examination of reflexes and sensitivity;
- X-ray examination;
- MRI – magnetic resonance imaging;
- CT – computed tomography of the spine.
Stages of osteochondrosis disease
This disease has four stages:
- First stageOsteochondrosis does not always manifest itself immediately, and the affected person may not even be aware of the developing disease. Overloading or incorrect loading of the spine results in what is known as "drying out of the intervertebral disc" when the moisture content of the intervertebral disc decreases. Serious destruction of the intervertebral disc has not yet occurred.
- Second floorcharacterized by a reduction in the distance between vertebrae, which can lead to pinched nerves. Reducing the distance leads to sagging of the ligaments and muscles, which increases the mobility of the vertebrae, causing them to shift or slip. During an exacerbation of the disease, acute and aching pain occurs.
- Third sectioncharacterized by negative changes in the spine, such as arthrosis, scoliosis, etc. The patient feels stiffness in some parts of the spine. Depending on the area of the disease, numbness and tingling may occur in the lower and upper extremities.
- Fourth stagethe most dangerous, which often leads to disability of the patient. In order to fix the "wandering" vertebrae, they begin to grow over with bone tissue and fix them. Due to the growth of new bone tissue, nerves are pinched. The cartilage tissue also thickens. Since the spine is injured, this stage involves irreversible changes in the spinePatients' mobility decreases and it becomes difficult for them to move; even the smallest movements can lead to severe, unbearable pain.
Treatment of osteochondrosis
Proper treatment of spinal osteochondrosis is complex therapy that depends on the stage of the disease.
In the early stages of the disease, complete recovery can even be achieved with the help of diet, physiotherapy and physiotherapy.
Massage is also indicated for osteochondrosis in the non-acute stage. Carrying out a massage has a positive effect on blood circulation in the spine and the entire back, pain and inflammation are relieved. If you use special oils and ointments during this procedure, you can achieve even more positive results from your back pain.
During an exacerbation and in acute stages, drug treatment cannot be avoided. If the disease is advanced, surgical intervention is often necessary. Typically, such operations involve the removal of an intervertebral hernia, which occurs due to improper or incomplete treatment and causes such an unpleasant complication as an inguinal hernia.
Undoubtedly, every person is unique and the disease progresses differently in everyone and requires individual treatment. But still, let's talk about the general method of treatment:
- Relieves pain and inflammation. Such unpleasant symptoms can be alleviated with the help of medications that have anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects.
- Restoring vitamin balance with the help of B vitamins. In addition, such vitamin complexes help to improve the patency of the nerves of the spine.
- To restore cartilage tissue and intervertebral discs, chondroprotectors are prescribed;
- To reduce muscle spasms, muscle relaxants are prescribed to relieve tension;
- For osteochondrosis, drugs that improve blood supply are also prescribed. They help improve blood circulation in the spine.
Very often, sedatives are prescribed to maintain a person's psychoemotional background.
In addition to medications, physiotherapy is prescribed. They help make treatment more effective and speed up the patient's recovery process. These procedures include magnetic therapy, ultrasound, electrophoresis and others.
After relieving severe pain and inflammation, exercise therapy is indicated. Physiotherapy is one of the most effective ways to improve the condition and quality of life of a patient with osteochondrosis.
There are other, less common treatments:
- Manual therapy;
- spinal traction;
- Acupuncture;
The three treatment methods listed above should be treated with caution, as it is not uncommon for pseudo-specialists and fraudsters without medical training to worsen the patient's condition to the point where he becomes bedridden.
There are also folk methods of treating osteochondrosis: various natural ointments, herbal teas, baths with medicinal herbs. This therapy is less effective than drug therapy, but with complex treatment it can produce significant results.
Prevention of osteochondrosis
The following recommendations will help avoid exacerbation of osteochondrosis and prevent the progression of the disease:
- If you have a sedentary job or spend a lot of time sitting, you need to take a break with a light warm-up every 30-45 minutes;
- Do moderate exercise regularly (gymnastics, exercise therapy, walking, swimming are very useful);
- Never overload your body by physically lifting too heavy a weight. If you still need to lift weights, try to avoid sudden movements. You can also use special belts or corsets. This will support your back and reduce the risk of a back injury when lifting heavy objects.
- For sleeping, it is better to choose an orthopedic mattress, which you can ask your doctor about;
- If you need to sit for long periods of time, it is a good idea to choose a high-quality chair or chair, preferably orthopedic;
- Try to eat right and balanced so that your body gets all the necessary nutrients;
- Try to avoid stressful situations, be happier and enjoy life;
- Try to wear comfortable, high-quality shoes without high heels.
With the right approach to the disease, its progression can be stopped. Regular and, most importantly, correct physical activity (physiotherapy and gymnastics), as well as a balanced diet, will help you forget about such an unpleasant and insidious disease as osteochondrosis.